जब आप Unix timestamps के साथ काम कर रहे हों, तो seconds vs milliseconds vs microseconds के बीच चुनाव आपके application की performance, storage requirements, और precision को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से प्रभावित कर सकता है। जबकि Unix timestamps पारंपरिक रूप से 1 जनवरी, 1970 के बाद से seconds में समय को मापते हैं, आधुनिक applications को अक्सर events को log करने, API response times को मापने, या distributed systems को synchronize करने के लिए उच्च precision की आवश्यकता होती है। यह guide प्रत्येक precision level के बीच व्यावहारिक अंतर को समझाती है और आपके specific use case के लिए सही चुनाव करने में मदद करने के लिए स्पष्ट मानदंड प्रदान करती है।
विषय सूची
तीन Precision Levels को समझना
Unix timestamps समय को एक single number के रूप में represent करते हैं जो epoch time reference point से count करता है। Precision level यह निर्धारित करती है कि आप time intervals को कितनी बारीकी से माप सकते हैं।
Seconds (10 अंक): Original Unix timestamp format एक 32-bit या 64-bit integer का उपयोग करता है जो पूरे seconds को represent करता है। एक typical value 1704067200 की तरह दिखती है, जो subdivisions के बिना समय में एक exact moment को represent करती है।
Milliseconds (13 अंक): यह format seconds की value को 1,000 से multiply करता है, तीन decimal places की precision जोड़ता है। वही moment 1704067200000 बन जाता है। JavaScript का Date.now() function by default इस format में timestamps return करता है।
Microseconds (16 अंक): मुख्य रूप से extreme precision की आवश्यकता वाले systems में उपयोग किया जाता है, यह format seconds को 1,000,000 से multiply करता है। Value 1704067200000000 बन जाती है। Python के time.time_ns() जैसी languages nanosecond precision (19 अंक) के साथ भी काम कर सकती हैं, हालांकि microseconds अधिकांश applications के लिए practical upper limit को represent करते हैं।
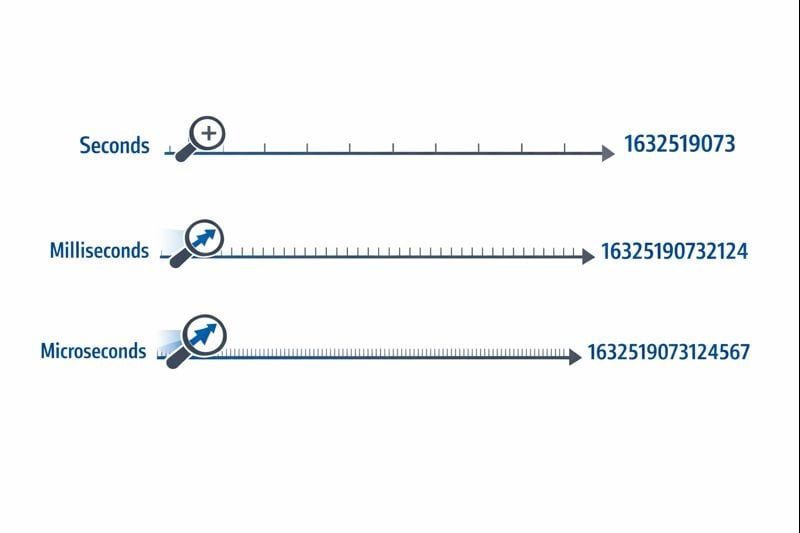
आप जो precision level चुनते हैं वह सीधे आपके database size, memory consumption, और query performance को प्रभावित करती है। जैसे-जैसे आपका application scale होता है, ये constraints critical हो जाती हैं।
Storage Requirements
एक 32-bit integer (4 bytes) Year 2038 problem होने तक second-level timestamps को store कर सकता है। अधिकांश modern systems इस limitation से बचने के लिए 64-bit integers (8 bytes) का उपयोग करते हैं।
- Seconds: एक signed 64-bit integer (BIGINT) के लिए 8 bytes
- Milliseconds: एक signed 64-bit integer (BIGINT) के लिए 8 bytes
- Microseconds: एक signed 64-bit integer (BIGINT) के लिए 8 bytes
जबकि प्रत्येक precision level modern databases में same 8-byte storage का उपयोग करती है, actual impact indexing और query operations से आता है। बड़ी numbers को comparison operations के लिए अधिक CPU cycles की आवश्यकता होती है, और index B-trees बड़ी key values के साथ थोड़ी कम efficient हो जाते हैं।
Database Query Performance
जब आप databases में Unix timestamps के साथ काम कर रहे हों, तो precision level range queries और sorting operations को प्रभावित करती है। एक database 10-digit numbers की तुलना 16-digit numbers की तुलना से marginally faster करता है, हालांकि difference केवल millions of rows पर noticeable होता है।
अधिक critically, आपके database में precision levels को mix करना conversion overhead create करता है। यदि आपकी application layer millisecond timestamps भेजती है लेकिन आपका database seconds store करता है, तो हर query को 1,000 से division की आवश्यकता होती है, जो efficient index usage को prevent करता है।
Network और API Considerations
JSON payloads timestamps को strings या numbers के रूप में transmit करते हैं। एक 16-digit microsecond timestamp एक 10-digit second timestamp की तुलना में 6 extra characters जोड़ता है। Millions of API calls में, यह measurable bandwidth costs और serialization overhead जोड़ता है।
Seconds का उपयोग कब करें
Second-level precision अधिकांश user-facing features के लिए best choice बनी रहती है जहां human perception relevant time scale को define करता है।
Ideal Use Cases
- Social media posts और comments: Users एक second से कम के differences को perceive नहीं करते
- Scheduled tasks और cron jobs: अधिकांश automation minute या hour boundaries पर run होता है
- User authentication tokens: Session expiry को sub-second accuracy की आवश्यकता नहीं होती
- Content publication dates: Articles, videos, और blog posts second-level precision का उपयोग करते हैं
- Booking और reservation systems: Appointments typically minute या hour slots के साथ align होते हैं
Actionable Implementation Steps
Second-level timestamps को effectively implement करने के लिए:
- Signed 64-bit integers store करने के लिए अपने database में
BIGINTcolumns का उपयोग करें - "पिछले 24 घंटों से posts" जैसी range queries के लिए timestamp columns पर indexes create करें
- JavaScript में, millisecond timestamps को convert करें:
Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) - Python में, उपयोग करें:
int(time.time()) - API specifications में अपनी precision choice को document करें ताकि consumers को पता हो कि 1,000 से multiply करना है या नहीं
Milliseconds का उपयोग कब करें
Millisecond precision तब necessary हो जाती है जब आपको ऐसे events को track करने की आवश्यकता होती है जो प्रति second कई बार occur होते हैं या एक second से छोटी durations को measure करना होता है।
Ideal Use Cases
- API response time monitoring: Track करना कि endpoints 200ms या 800ms के भीतर respond करते हैं या नहीं
- Financial transactions: Trades या payment processing steps के exact sequence को record करना
- Real-time messaging: Same second में भेजे गए chat messages को order करना
- Video streaming analytics: Playback events और buffering incidents को record करना
- Distributed system coordination: Multiple servers में events को synchronize करना
Actionable Implementation Steps
Millisecond-level timestamps को implement करने के लिए:
- Clear documentation के साथ अपने database में
BIGINTcolumns का उपयोग करें कि values milliseconds को represent करती हैं - JavaScript में, सीधे
Date.now()का उपयोग करें (यह by default milliseconds return करता है) - Python में, उपयोग करें:
int(time.time() * 1000) - Discord timestamps और similar platforms के लिए, milliseconds standard precision provide करते हैं
- यह ensure करने के लिए application-level validation जोड़ें कि timestamps reasonable ranges के भीतर आते हैं (accidentally seconds या microseconds में नहीं)
Real-World Constraints
Millisecond precision एक subtle challenge introduce करती है: सभी systems truly accurate millisecond timestamps generate नहीं करते। Operating system clock resolution vary करता है, और virtualized environments केवल हर 10-15 milliseconds में अपनी clocks को update कर सकते हैं। यदि underlying clock true millisecond accuracy को support नहीं करती है तो आपके timestamps false precision दिखा सकते हैं।
Microseconds का उपयोग कब करें
Microsecond precision अधिकांश applications के लिए overkill है लेकिन extreme accuracy की आवश्यकता वाले specialized domains में essential हो जाती है।
Ideal Use Cases
- High-frequency trading systems: Order book updates को record करना जो प्रति second हजारों बार occur होते हैं
- Performance profiling और benchmarking: Microsecond range में function execution times को measure करना
- Scientific data collection: Sensor readings या experimental measurements को log करना
- Network packet analysis: Security या debugging के लिए network events की exact timing को capture करना
- Audio/video processing: Frame या sample level पर multimedia streams को synchronize करना
Actionable Implementation Steps
Microsecond-level timestamps को implement करने के लिए:
- Verify करें कि आपकी programming language और database microsecond precision को support करते हैं (सभी नहीं करते)
- Python में, उपयोग करें:
int(time.time() * 1_000_000) - C/C++ में,
CLOCK_REALTIMEके साथgettimeofday()याclock_gettime()का उपयोग करें - High-precision timestamps के लिए design किए गए InfluxDB या TimescaleDB जैसे specialized time-series databases का उपयोग करने पर विचार करें
- Precision requirement को clearly document करें, क्योंकि अधिकांश developers by default milliseconds assume करेंगे
Real-World Constraints
Microsecond timestamps distributed systems में significant challenges create करते हैं। Network latency typically milliseconds में measure होती है, जो GPS-synchronized clocks जैसे specialized hardware के बिना servers में microsecond-level synchronization को nearly impossible बनाती है। यदि आपका application multiple data centers में run होता है, तो microsecond precision false accuracy provide कर सकती है।
Case Study: E-commerce Order Processing System
Hypothetical Case Study:
निम्नलिखित example timestamp precision के लिए real-world decision-making को demonstrate करता है। जबकि company fictional है, technical constraints और solutions common scenarios को represent करते हैं।
ShopFast, एक mid-sized e-commerce platform, ने initially अपने order processing system को second-level Unix timestamps का उपयोग करके build किया। जैसे-जैसे वे peak hours के दौरान प्रति minute 500 orders process करने के लिए scale हुए, उन्हें एक critical problem का सामना करना पड़ा।
The Problem
Same second के भीतर placed किए गए multiple orders को reliably sort नहीं किया जा सकता था। जब customers support से contact करके पूछते "कौन सा order पहले गया?", तो system एक definitive answer provide नहीं कर सकता था। अधिक critically, उनके fraud detection system को flag करने की आवश्यकता थी जब same credit card को एक short window में multiple purchases के लिए उपयोग किया जाता था, लेकिन second-level precision ने इसे unreliable बना दिया।
The Analysis
Engineering team ने विभिन्न system components में अपनी requirements को evaluate किया:
- Order creation timestamps: Proper sequencing के लिए millisecond precision की आवश्यकता थी
- Product catalog last_updated fields: Second precision sufficient रही
- Payment processing logs: Fraud detection के लिए millisecond precision की आवश्यकता थी
- Customer account creation dates: Second precision sufficient रही
- API request logging: Performance monitoring के लिए millisecond precision की आवश्यकता थी
The Solution
अपने entire database को milliseconds में convert करने के बजाय, उन्होंने एक hybrid approach implement किया:
- Existing values को 1,000 से multiply करके
orders.created_atको seconds से milliseconds में migrate किया - Order-related endpoints के लिए millisecond timestamps को accept और return करने के लिए अपनी API layer को update किया
- Migration scope को minimize करने के लिए user-facing timestamps (account creation, last login) को seconds में छोड़ दिया
- यह distinguish करने के लिए clear documentation जोड़ी कि कौन से fields किस precision का उपयोग करते हैं
- Accidental precision mismatches को catch करने के लिए application-level validation implement किया
The Results
Migration के बाद, system reliably orders को sequence कर सकता था और fraud patterns को detect कर सकता था। Storage increase negligible था (existing numbers में तीन digits जोड़ना), लेकिन improved functionality ने migration effort को justify किया। Query performance virtually identical रही क्योंकि उन्होंने proper indexing maintain की।
Key lesson: आपको अपने entire application में uniform precision की आवश्यकता नहीं है। Theoretical concerns के बजाय actual requirements के आधार पर प्रत्येक specific use case के लिए appropriate level चुनें।
Timestamp Precision चुनने के लिए Best Practices
अपने applications में Unix timestamps implement करते समय इन guidelines को follow करें:
1. Seconds से शुरू करें, केवल आवश्यक होने पर Upgrade करें
जब तक आपके पास finer granularity के लिए एक specific requirement न हो, second-level precision को default करें। Premature optimization development time waste करता है और unnecessary complexity create करता है। अधिकांश applications को कभी भी sub-second precision की आवश्यकता नहीं होती।
2. Domains के भीतर Consistency बनाए रखें
Related timestamps के लिए same precision level का उपयोग करें। यदि आपकी orders table milliseconds का उपयोग करती है, तो आपकी order_items और order_payments tables को match करना चाहिए। Precision levels को mix करना constant conversion force करता है और bugs create करता है।
3. अपनी Precision Choice को Document करें
अपने database schema, API documentation, और code में comments जोड़ें जो explain करें कि timestamps seconds, milliseconds, या microseconds को represent करते हैं या नहीं। Context के बिना 1704067200000 की एक timestamp value ambiguous है।
4. Timestamp Ranges को Validate करें
Precision errors को catch करने के लिए validation implement करें। Seconds में एक timestamp current dates के लिए roughly 1,000,000,000 (September 2001) और 2,000,000,000 (May 2033) के बीच fall होनी चाहिए। एक millisecond timestamp approximately 1,000 गुना बड़ी होनी चाहिए। इन errors को early catch करना data corruption को prevent करता है।
5. अपने Database के Native Types पर विचार करें
कुछ databases built-in precision के साथ native timestamp types offer करते हैं। PostgreSQL की TIMESTAMP type internally microsecond precision store करती है। MySQL की DATETIME type version 5.6.4 से microseconds को support करती है। ये native types अक्सर raw integers store करने की तुलना में better query optimization provide करते हैं।
6. Distributed Systems में Clock Drift के लिए Account करें
यदि आप different servers द्वारा generated timestamps की तुलना कर रहे हैं, तो proper clock synchronization के बिना even millisecond precision misleading हो सकती है। सभी servers पर NTP (Network Time Protocol) implement करें और distributed systems में events को order करने के लिए logical clocks (जैसे Lamport timestamps या vector clocks) का उपयोग करने पर विचार करें।
7. Conversion Logic को Thoroughly Test करें
Precision levels के बीच convert करते समय, negative timestamps (1970 से पहले की dates), बहुत बड़ी timestamps (far future dates), और आपके integer types की boundaries जैसे edge cases को test करें। एक 32-bit integer 2038 से परे millisecond timestamps को store नहीं कर सकता।
8. Year 2038 Problem के लिए Plan करें
यदि आप second-level timestamps का उपयोग कर रहे हैं, तो ensure करें कि आप 64-bit integers का उपयोग कर रहे हैं, 32-bit का नहीं। Year 2038 problem केवल 32-bit signed integers को affect करती है। Unix timestamp tutorial best practices को follow करना आपके application को future-proof करने में मदद करता है।
निष्कर्ष
Unix timestamps के लिए seconds vs milliseconds vs microseconds के बीच चुनाव आपकी specific application requirements पर निर्भर करता है, arbitrary technical preferences पर नहीं। Second-level precision अधिकांश user-facing features को efficiently handle करती है, millisecond precision API monitoring और real-time coordination को enable करती है, और microsecond precision specialized high-frequency applications को serve करती है। अपनी needs को meet करने वाले simplest option से शुरू करें, related data के भीतर consistency maintain करें, और अपनी choices को clearly document करें। Storage, performance, और precision के बीच practical trade-offs को समझकर, आप informed decisions ले सकते हैं जो आपके application की growth के साथ scale करते हैं।
Timestamp Formats के बीच तुरंत Convert करें
Timestamp Formats के बीच तुरंत Convert करें
हमारे free Unix timestamp converter के साथ seconds, milliseconds, और microseconds के बीच switch करें। किसी coding की आवश्यकता नहीं।
हमारा Free Tool आज़माएं →